US and India Tax Systems: Expats and visa holders in the United States and India face distinct tax obligations based on their residency status, income sources, and the tax treaties between the two countries. Below is an overview of the critical features of the tax systems in both nations regarding expatriates.
Key Takeaways
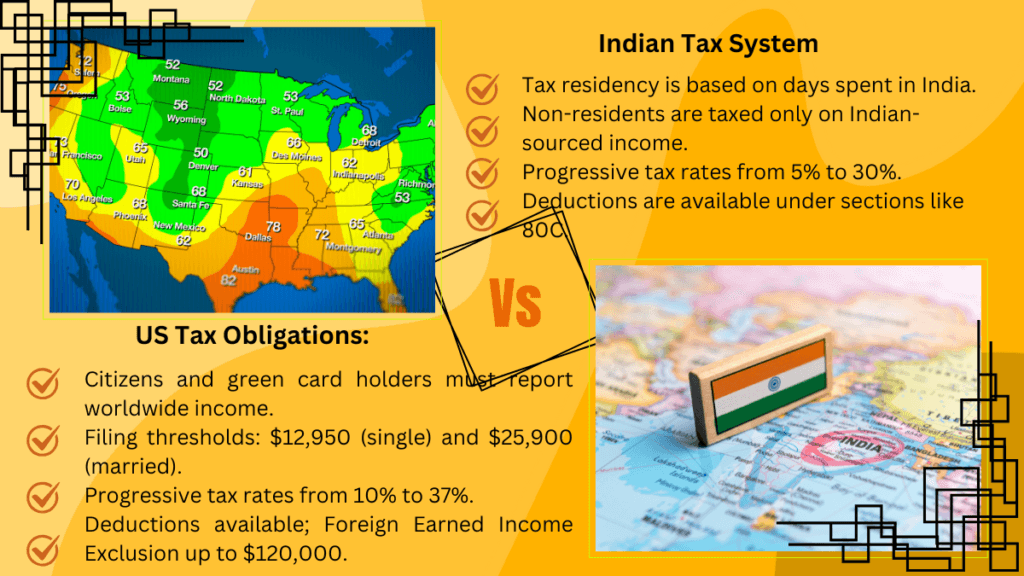
- US Tax Obligations: Citizens and green card holders must report worldwide income.
- Filing thresholds: $12,950 (single) and $25,900 (married).
- Progressive tax rates from 10% to 37%.
- Deductions are available; Foreign Earned Income Exclusion is up to $120,000.
- Indian Tax Obligations: Tax residency is based on days spent in India.
- Non-residents are taxed only on Indian-sourced income.
- Progressive tax rates from 5% to 30%.
- Deductions are available under sections like 80C.
- Filing Requirements: US expats receive an extension to June 15 but must pay by April 15.
- Indian residents earning over INR 500,000 must file returns.
- Double Taxation Relief: Both countries have agreements to mitigate double taxation.
- Consult Professionals: Hire tax Experts who are familiar with both systems.

US Tax Systems for Expats
Tax Filing Requirements:
- Worldwide Income: US citizens and green card holders must report their worldwide income, regardless of salary and where they live. This includes compensation, intrigue, profits, and self-employment wages.
- Filing Thresholds: The filing threshold for the tax year 2023 for single filers under 65 is $12,950. Married couples filing jointly if their combined total income is over $25,900
- Tax Forms: Essential forms include Form 1040 for individual income tax returns and Form 8938 for reporting foreign financial assets if they exceed certain thresholds
Tax Rates As per US Tax Systems:
- The US has a progressive tax system, meaning the tax rate increases as income rises. For example, if you earn up to $11,600. You’ll pay a tax rate of 10%. But if your income exceeds $462,500, you’ll face a higher tax rate of 37%.
- Detailed Taxable Income Range in the US for the Year 2024
| Tax Rate | 2024 Taxable Income Range | ||
| 10% | $0 – $23,200 | ||
| 12% | $23,201 – $94,300 | ||
| 22% | $94,301 – $201,050 | ||
| 24% | $201,051 – $383,900 | ||
| 32% | $383,901 – $487,450 | ||
| 35% | $487,451 – $731,200 | ||
| 37% | $731,201+ |
The tax rates above are in general categories, and there are some differences in other categorie,s such as for single filers, married couples filing jointly, married couples filing separately, and for head of household.
Deductions and Credits
- US: Various deductions are available based on filing status and income level. Expats can claim foreign tax credits using Form 1116 for taxes paid in India.
Deadlines and Penalties:
How to Take Advantage of the Tax Deadline Extension? IRS Announces Major Tax Deadline Extension for 2024: What You Need to Know
- Expats get a programmed expansion to record until June 15 but must pay any charges owed by April 15 to maintain a strategic distance from penalties. Failure-to-file punishments can reach up to 25% of unpaid charges.
Relief from Double Taxation:
- The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) allows eligible expats to exclude up to $120,000 of foreign-earned income from US taxation. Also, the US has a double taxation agreement with India helps mitigate tax liabilities for those earning in both countries.

Indian Tax Systems for Expats
Tax Residency Status:
- An individual is considered a tax resident in India if they stay in the country for 182 days or more during a financial year or for 60 days or more during that year and have been in India for 365 days or more over the preceding four years. Non-residents are taxed only on income sourced within India.
Also Read Benefits of NIL Tax Return – Nil ITR: Why should you file a Nil ITR? Ultimate Benefits
Income Tax Rates As per the Indian Tax Systems:
- India employs a dynamic charge framework, meaning charge rates increase with higher pay levels. For example, if you earn up to INR 250,000, you won’t pay any assess. If your pay surpasses INR 1,000,000, you’ll be saddled at 30% and any additional charges that may apply. Your actual charge rate can vary depending on the derivations you claim from the different assessment plans.
- Detailed Taxable Income Range in India in the Year 2024 (The Old Regime and The New Regime)
| New Tax Regime: | Old Tax Regime: | |||
| Tax Slab for FY 2024-25 | Tax Rate | Tax Slab for FY 2024-25 | Tax Rate | |
| Upto ₹ 3 lakh | Nil | Up to Rs 2,50,000 | NIL | |
| ₹ 3 lakh – ₹ 7 lakh | 5% | Rs 2,50,001 – Rs 5,00,000 | 5% | |
| ₹ 7 lakh – ₹ 10 lakh | 10% | Rs 5,00,001 to Rs 10,00,000 | 20% | |
| ₹ 10 lakh – ₹ 12 lakh | 15% | Rs 10,00,001 and above | 30% | |
| ₹ 12 lakh – ₹ 15 lakh | 20% | — | — | |
| More than 15 lakh | 30% | — | — | |
Tax rates as above are in a general category; the new tax system is fixed, but in the old tax system, there are some differences based on the age of taxpayers.
Deductions and Credits under Both Tax Systems
- India: Deductions are available under sections like 80C for investments in specified savings schemes. Income below certain thresholds is exempt from tax.
Also Read – Tax Analysis on Budget: Powerful Guidelines & Tips for FY 2024-25
Filing Requirements:
- All pay earned by Indian inhabitants is subject to Indian tax collection. Non-residents are saddled as they are on Indian-sourced pay. For the appraisal year 2023-24, people gaining over INR 500,000 must record an assessed filing in India.
Social Security Contributions:
- Expatriates working in India are usually required to make social security contributions, which are mandatory under Indian law. You must contribute to the country’s social security system if employed in India.
Double Taxation Relief:
- Unlike the US system, expats in India have the advantage of the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) between India and the US. This agreement allows you to offset taxes you pay in one country against the taxes you owe in the other, helping to reduce your overall tax burden.
Conclusion of US and Indian tax systems

Understanding the subtleties of US and Indian assessment frameworks is vital for exiles and visa holders. Each nation has its own set of rules concerning residency status, assessable wage, and recording necessities. Also, twofold tax assessment settlements and outside wage prohibitions can give noteworthy alleviation to people exploring these complex frameworks. Expats should consider counselling with charge experts commonplace in both locales to guarantee compliance and optimize their tax circumstances.
Hi there! I am Sudip Sengupta, the face behind “Tfin Career”. Tfin Career is a sole proprietorship finance and consulting firm that makes complex tax and financial concepts easy to understand for everyone. With more than 21 years of experience in the field, I have noticed that people cannot make the right decisions in this field. So, I decided to create “Tfin Career” to help individuals and businesses alike. Here I urge those who are confused to make better choices. Also, it is good news for my dear clients and every visitor that I/we are going to start a training module for those who want to choose a career path in Finance and Taxation. Just follow my website.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!