The 2025 Capital gains tax can significantly impact your profits when selling investments, real estate, or other assets. With 2025’s inflation-adjusted tax brackets and potential policy changes, understanding the rules is crucial to minimizing your tax bill.
This updated guide clarifies 2025 capital gains tax rates, includes real-world examples, and provides actionable strategies to reduce liabilities—backed by IRS rules and financial experts 168.
1. 2025 Capital Gains Tax Rates (Updated for Inflation)

A. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Rates
Short-Term Gains (held ≤1 year): Taxed as ordinary income (10%–37%).
Long-Term Gains (held >1 year): Preferential 0%, 15%, or 20% rates, based on income 14.
Long-Term: 2025 Capital Gains Tax Brackets
| Filing Status | 0% Rate | 15% Rate | 20% Rate |
| Single | ≤$48,350 | 48,351–48,351–533,400 | >$533,400 |
| Married (Joint) | ≤$96,700 | 96,701–96,701–600,050 | >$600,050 |
| Head of Household | ≤$64,750 | 64,751–64,751–566,700 | >$566,700 |
Example:
A single filer with 50,000 taxable income sells stocks held∗∗3 years∗∗for a∗∗50,000 taxable income sells stocks held∗∗3 years∗∗for ∗∗10,000 profit**.
Tax: 10,000×1510,000×151,500** (vs. 22% if short-term).
2. Key Changes for 2025 Capital Gains Tax

Higher Income Thresholds: Adjusted for ~2.8% inflation 611.
Potential TCJA Sunset: If Congress does not act, long-term rates could revert to pre-2018 levels, potentially increasing the 20% top rate.
Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT): Still 3.8% for high earners (MAGI >200K single / 200K single / 250K joint).
Capital Gains Tax Simplified: Short-Term vs. Long-Term & Ways to Reduce Your Tax Bill
3. How to Calculate 2025 Capital Gains Tax (With Examples)

Formula: Capital Gain = Selling Price − (Purchase Price + Improvements + Selling Costs)
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Stocks Bought 100 shares in 2023: $5,000
Sold in 2025: $12,000
Gain: 12,000−12,000−5,000 = $7,000
Tax (15% bracket): 7,000×157,000×151,050** 18.
Example 2: Real Estate Bought home in 2020: $400,000
Renovations: $50,000
Sold in 2025: **600,000∗∗after 600,000∗∗(after 30,000 fees)
Taxable Gain: 600K−(600K−(400K + 50K+50K+30K) = $120,000
Tax (20% bracket): 120,000×20120,000×2024,000**.
4. How to Reduce 2025 Capital Gains Tax Liabilities: A Detailed Guide
Capital gains taxes can take a significant bite out of your investment profits, but with proper planning, you can legally minimize your tax burden. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of the most effective strategies for reducing capital gains taxes in 2025, complete with detailed explanations and real-world examples.
Also read, How to Pay 0% Capital Gains Tax (Legally) in 2025: What You Need to Know
Strategy 1: Hold Assets for More Than One Year
Why It Works
The difference between short-term and long-term capital gains tax rates is substantial. Short-term gains (assets held ≤1 year) are taxed as ordinary income (10%-37%), while long-term gains (assets held >1 year) benefit from preferential rates of 0%, 15%, or 20%.
Example & Savings
- Scenario:You sell stocks for a $50,000 profit.
- Short-term (≤1 year):Taxed at 24% (assuming you’re in this bracket) =$12,000 tax
- Long-term (>1 year):Taxed at 15% =$7,500 tax
Savings:$4,500by holding the investment for just a few months longer.
Key Considerations
- The exact savings depend on your income bracket.
- For high earners (over $ 533,400single or $600,050 married), the long-term rate is 20% (still better than ordinary income rates).
Strategy 2: Tax-Loss Harvesting
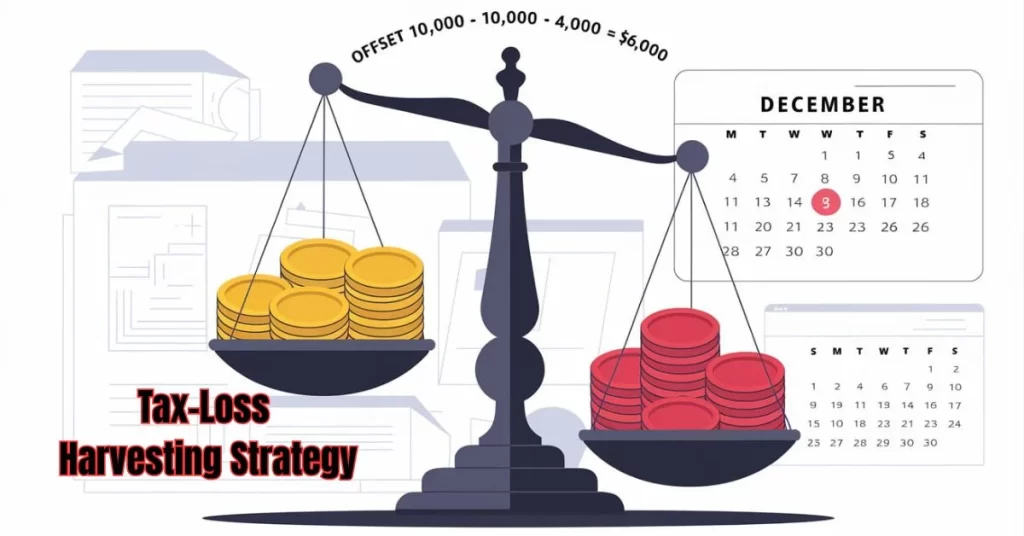
How It Works
Sell losing investments to offset gains from winning ones. The IRS allows you to deduct capital losses against capital gains, reducing your taxable income.
Example
- You have:
- $10,000 gainfrom Stock A
- $4,000 lossfrom Stock B
- Net taxable gain:10,000−10,000−4,000 =$6,000
Advanced Tactics
- Carry Forward Excess Losses:If losses exceed gains, you can deduct up to$3,000/yearagainst ordinary income and carry forward the rest indefinitely.
- Avoid Wash Sales:Do not repurchase the same or a “substantially identical” asset within 30 days before or after the sale; otherwise, the loss will be disallowed.
Strategy 3: Use Tax-Advantaged Accounts
A. Roth IRAs & 401(k)s
- Tax-Free Growth:All gains in Roth accounts are tax-free if withdrawn after age 59½ (and held for 5+ years).
- No Capital Gains Tax:Selling investments within a Roth IRA triggers no tax, regardless of holding period.
B. 1031 Exchange (Real Estate Only)

- How It Works:Reinvest proceeds from a sold property into a “like-kind” property within180 daysto defer capital gains taxes indefinitely.
- Example:Sell a rental property for 500,000 (with 500,000 200,000 gain) and buy another for 600,000→∗∗600,000→∗∗0 immediate tax**.
- Key Rules:
- Must identify replacement property within45 days.
- Must be investment/business property (not personal residence).
Strategy 4: Primary Home Exclusion

The Rule
- Single filers:Exclude up to$250,000of capital gains.
- Married filers:Exclude up to$500,000.
Requirements
- Owned the home forat least 2 years.
- Lived in it as your primary residence for2 of the last 5 yearsbefore sale.
- I haven’t used this exclusion for another home in the past two years.
Example
- Bought home for 300,000, sold for 300,000, sold for 800,000 → $500,000 gain.
- Single filer:500,000−500,000−250,000 exclusion =$250,000 taxable gain.
- Married filer:500,000−500,000−500,000 exclusion =$0 tax.
Strategy 5: Gift Appreciated Assets

How It Works
Transfer assets to family members in lower tax brackets (e.g., children or retired parents), who can then sell them and pay little or no capital gains tax.
Example
- You want to sell stock with a 50,000 gain (you′re in the 2050,000 gain (you′re in the 2010,000 tax**).
- Instead, gift the stock to your college-age child (who has a $20,000 income).
- They sell it and pay0% tax(since their income is below $48,350 for 2025).
Key Rules
- Gifts over **18,000 / year (2025 limit)∗∗ may require filing a gift tax return (but no tax owed until life time exemption of 18,000 / year(2025 limit)∗∗ may require filing a gift tax return (but no tax owed until life time exemption of 13.61 million is exceeded).
- The recipient inherits your original cost basis, except for inherited assets, which receive a “step-up” basis.
Bonus Strategy: Charitable Donations of Appreciated Assets

How It Works
Donate stocks/real estate held >1 year to a qualified charity. You:
- Avoid capital gains taxon the appreciation.
- Get a tax deductionfor the full market value.
Example
- Bought stock for 10,000, now worth 10,000, now worth 50,000.
- Donate it instead of selling:
- **0 capital gains tax∗∗ (vs. zero capital gains tax∗∗(vs.8,000 tax if sold in 20% bracket).
- $50,000 charitable deduction(if you itemize).
Final Tips for Reducing Capital Gains Tax Liabilities in 2025

- Track Your Cost Basis:Keep records of purchase prices, improvements, and fees.
- Time Your Sales:If possible, spread gains across multiple years to stay in lower brackets.
- Consult a Tax Pro:For complex situations (significant gains, inherited assets, etc.).
By implementing these strategies, you could savethousandsin capital gains taxes. Which one will you use first?
Notable Cases & State Taxes
Some states imposeadditional taxes:
| State | Max Rate | Notes |
| California | 13.3% | Highest in U.S. |
| New York | 10.9% | NYC adds extra |
| Washington | 7% | Only on gains >$250K |
| Texas/Florida | 0% | No state income tax |
Collectables (art, gold): Taxed at 28%.
Final Checklist for 2025
✅ Hold investments for over 1 year to benefit from lower rates.
✅ Document home improvements (adds to cost basis).
✅ Use tax-advantaged accounts (e.g., Roth IRA).
✅ Offset gains with losses (harvest losses annually).
✅ Consult a CPA for complex transactions (e.g., 1031 exchanges).
Pro Tip: The IRS adjusts brackets annually—verify rates before filing 11.
For more details, refer to:
Kiplinger’s 2025 Capital Gains Tax Guide
Need personalized advice? A tax professional can help optimize your strategy. 🚀


